What is a 3D printer made of and how does it work?
Most modern 3D printers with CNC unit use the same approach to the 3D printing process. The components and individual parts of such devices may differ, but in general, the principles of construction and the design of the printers are almost the same.
- What is a 3D printer made of: main components
- Importance of correct assembly of 3D printer components
What is a 3D printer made of: main components
The principles of operation of 3D printers are similar to those previously used by Cartesian robots.
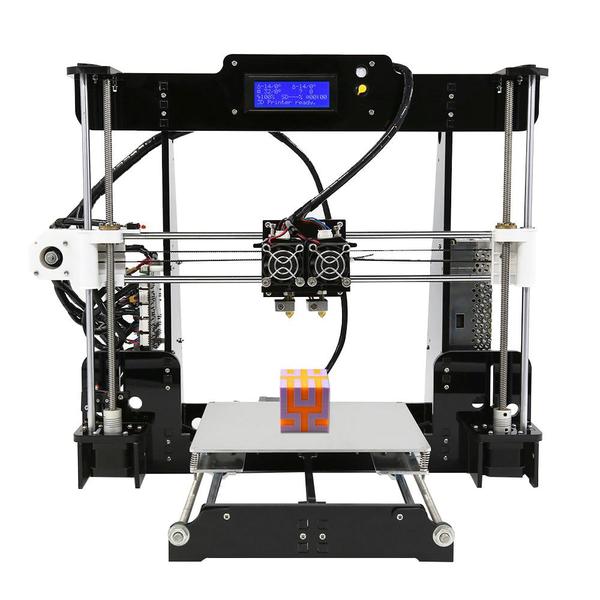
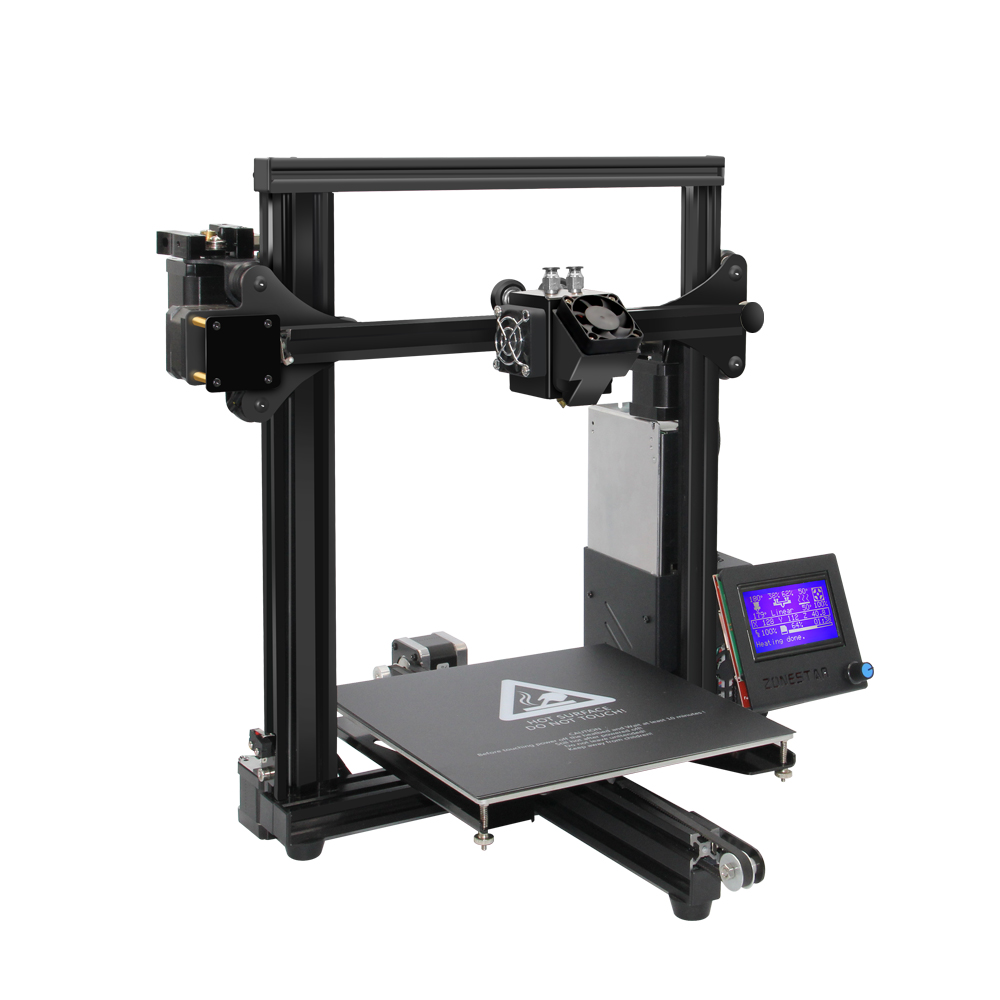
A 3D printer is a device whose parts can move linearly in three dimensions using the X, Y, and Z axes, called Cartesian coordinates. The movement is provided by small and highly accurate stepper motors. Their margin of error is no more than 1.8 degrees per step.
Like all other numerically controlled machines, 3D printers are controlled by a built-in controller. Its presence allows the movement of the device's printing head, which deposits molten plastic onto the work surface and ensures layer-by-layer printing of the item.
Many 3D printers are also equipped with timing belts and special rollers located on the X and Y axes. This technical addition allows for high-speed movement of the extruder while maintaining the precision of its positioning.
The main components of all 3D printers are:
- extruder (printing head);
- print table;
- a set of movement mechanisms;
- cooling system (fans);
- frame;
- control electronics.
Print table
The printer's work table is a surface onto which the molten material from the extruder is applied layer by layer during printing, creating the finished product. Depending on the model of the printing device, the size of the table can vary from 100 to 200 square millimeters.
The surface of the work table is made of glass or aluminum. These materials effectively distribute heat across the working surface, providing additional leveling of the product.
IMPORTANT! Glass provides a smoother surface, while aluminum tables have better heat conductivity.
To ensure that the printed model is securely fixed to the table, the surface of the platform is often covered with a layer of glue or a special film.
Frame
All components of the 3D printer are fixed on a special frame, which has high strength and rigidity.
It protects the components of the device from the negative effects of external factors and is responsible for the geometric integrity of the device, as well as the absence of play and vibrations that occur during printing.
3D printer frames can be either open, consisting only of aluminum guides, or closed, with the construction being complemented by organic glass or plywood.
Printing head
The most important component of any 3D printer using FDM technology is the printing head, which consists of two parts – the extruder and the heating element.
The extruder (cold-end) is a mechanism responsible for feeding material to the heater.
The heater (hot-end) is a component of the printing head responsible for melting and extruding the plastic filament through the nozzle, the diameter of which can vary from 0.14 to 0.60 mm.
IMPORTANT! An extruder of a specific model is designed to work with filaments of a specific diameter. This parameter should be considered when purchasing materials for printing.
To ensure uninterrupted material delivery to the extruder, the printing head is complemented by a stepper motor equipped with a system of shafts and gears. The controller, which manages the motor, is responsible for the speed of material feeding and its extraction when changing the material.
With active use of the printer, the nozzle opening can become clogged, reducing its throughput and print quality. The problem can be solved by cleaning the part or replacing it with a new one.
Most modern 3D printers are equipped with a single printing head, but in some models, there are multiple heads. Such printers are designed to print with two types of plastic at once.
Movement mechanism components
The movement mechanisms, consisting of motors and several guides combined into a system, are responsible for the movement of the platform and the printing head along the coordinate axes during printing.
Most of the time, three motors are sufficient to efficiently operate a 3D printer to move the head along the X and Y axes and the platform moving along the vertical (Z axis).
To convert the rotary motion of the motor rotors, the system is complemented by pulleys and toothed belts or threaded shafts, which are responsible for converting rotation into linear motion.
In budget models of 3D printers, the guides have a cylindrical shape. In more expensive variants, manufacturers prefer to use linear guides made of steel. The quality and cleanliness of the guide processing directly affect print precision.
The extreme positions of the work table and printing head are controlled by sensors installed in various places. The most accurate ones are LED sensors, photo diodes, and sensors whose principle of operation is based on magnetic radiation.
Electronics
The operation of all components of the 3D printer is controlled by a controller that recognizes G-code written by a special program and corrected by the user.
The program for the controller is created in a special editor in STL file format, which describes the 3D model. The text of the code uses special designations to encode the sequence and type of movements of the printing head and work table, as well as the need to turn on and off heating elements or cooling system.
Most controllers work on the Arduino platform, distinguished by its open architecture. In the hardware part, mostly Atmel or ATmega2560 microcontrollers are used.
To ensure efficient connection of modules and the microcontroller board, intermediate boards (RAMPS) with pin connectors to connect to the microcontroller board and connectors on the back for connecting necessary modules and external equipment are used.
All the listed components form a single compact block, which recognizes the model and is ready to work as part of an FDM 3D printer.
Some models of 3D printers can be controlled by personal computers or Wi-Fi network, while others are equipped with their control panel. Some printer models also have slots for memory cards or USB ports. Their presence allows you to load models into the device's memory without having to connect the printer to a personal computer.
Importance of correct assembly of 3D printer components
The final print quality directly depends on the precise and high-quality assembly of the components of the 3D printer. Poor assembly leads to the occurrence of play, missing motor steps, insufficient or excessive heating and cooling of the elements.
3D printing is a complex and lengthy process, the quality of which depends directly on the quality of the device's assembly. When purchasing a 3D printer, it is important to carefully check the condition of the main components and their suitability for solving specific tasks.