Delta 3D printer: self-assembly, setup, and maintenance.
3D printers with delta kinematics stand out among other models with high print speed of very complex parts. Such devices are quite expensive, but they can be self-assembled. Let's consider the assembly stages, setup, and nuances of using a delta printer.
- Which 3D printer is better — delta or Cartesian?
- How to build a Delta 3D printer with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
- Setup and calibration
- Errors in creation and tips on how to avoid them
Which 3D printer is better — delta or Cartesian?
Cartesian and delta printers are used for printing the same types of filaments. In addition to this, they have the same working parts (extruder, platform, motor), but their arrangement differs.
For Cartesian 3D printers, the movement of the extruder or platform is along the axes X, Y, and Z (Cartesian plane). In other words, the working elements move left, right, forward, backward, up, and down.
For delta 3D printers, a different movement system is built into the operation. The device is equipped with three brackets that support the extruder. The brackets themselves are attached to three vertical posts arranged in the form of a triangle. The extruder of a delta printer can move in all directions, and each bracket can only move vertically up and down.
By considering the structural features of both types of equipment, it can be established which one will be better to use for specific purposes. To do this, let's highlight the advantages and disadvantages of Cartesian and delta printers.
Pros and cons of a delta printer
Among the main advantages of a delta printer, we should highlight:
- very fast printing of complex items;
- high detail of thin and small parts of the item;
- easy replacement of the extruder.
Along with the advantages of a delta printer, it also has the following disadvantages:
- limited information about the operation, assembly, and setup of the device;
- complex assembly, setup, and calibration for the correct functioning of the printer;
- difficulties in selecting parameters and settings for printing complex objects at high speed.
Pros and cons of a Cartesian printer
Traditional printers, which operate based on the Cartesian coordinate system, have several positive properties when in use:
- stable printing results in mass production of products;
- a large amount of free information on the structure, operation, setup, and maintenance of the printer on thematic forums;
- the size of the created item is not limited, as a model for printing on a Cartesian printer can be divided into separate parts.
The main and substantial disadvantage of a Cartesian printer is the much slower printing speed compared to a delta device. This is because the Cartesian printer spends a lot of time accelerating and decelerating the system. As a result, the printing head moves more slowly to the necessary point.
How to make a Delta 3D printer with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
Before starting the assembly of a Delta printer, it is necessary to correctly select all the components. The following components are required to construct a functional device:
- frame with plastic bushings;
- guide rollers;
- heated table;
- stepper motors;
- RAMPS 1.4 extension board;
- mechanical limiters;
- Arduino Mega 2560 R3 microcontroller;
- M5 threaded rods;
- voltage regulator;
- 12 V power supply;
- extruder;
- optical limit switches;
- filament spool;
- two fans (for cooling parts and for cooling drivers).
- display and button with a 220 V terminal.
The assembly of the delta 3D printer is carried out in the following order:
- First, the frame and end supports are constructed. The top lead screws remain free.
- The voltage regulator is soldered to the power input. The microcontroller is installed, and the regulator is fastened behind it.
- The extension board is soldered separately to the legs. Mechanical limiters are installed in the correct polarity direction.
- Before flashing the printer, electronic components and optical limit switches are connected to the printer. Also, the table, extruder, fans, and filament spool are installed.
- The firmware for the printer is adjusted based on its dimensions. Also, during installation, it is important that all the rods are of the same length.
Tip. To make the rods equal in length, you need to wind identical pieces of rod on both sides of the hinge. Then, neodymium magnets are installed on the ready-made rod, and the rod is rotated until the hinges are precisely centered on the magnet. After adjusting all the rods, the adhesion thread on the hinge is fixed with glue.
Setup and calibration
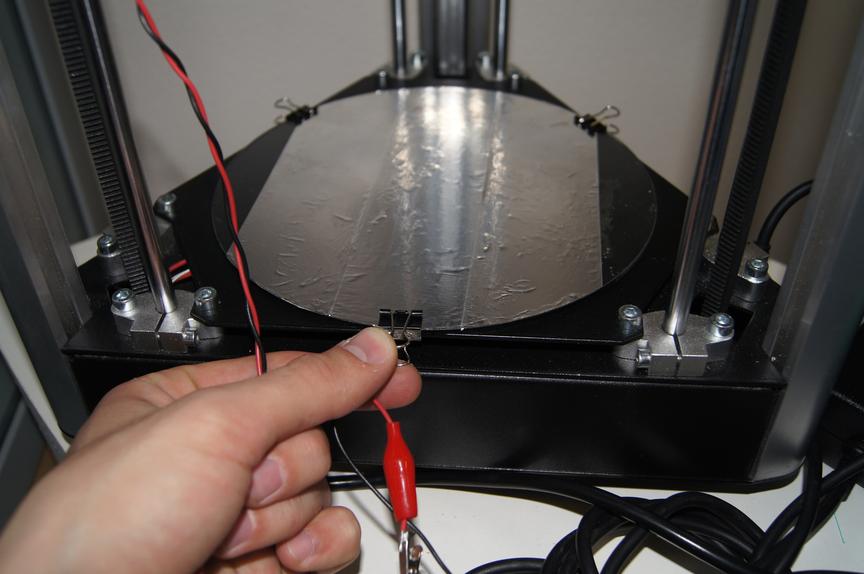
The most convenient way to calibrate a delta printer is with the help of the OpenDACT or Pronterface utility. These programs perform automatic calibration of the equipment using electrical contact between the metal nozzle and the table. This procedure is performed in three stages:
- Aluminum tape is stuck to the working table.
- One end of the cable is crimped into a socket, and the other two ends are fastened to a radiator and aluminum tape. Afterward, the three cable ends are connected to the 3D printer.
- Then, the printer is connected to a computer, from which the auto-calibration program is launched. The whole process can take a lot of time, as it requires adjusting all the necessary geometry parameters.
Before or after calibrating the printer, it is also necessary to calibrate the device's table. This allows for the achievement of maximum printing accuracy. Table calibration is done as follows:
- The table is heated to +90°C, the screws are tightened, and the printing head is moved to the center of the table. A sheet of white paper is placed directly under the extruder nozzle. The paper should not be pressed down too hard by the nozzle, but should not be loose under it either.
- After adjusting the central part of the table, the sheet is moved to the corners of the working surface and the table is calibrated in a similar way.
Errors in creation and tips on how to avoid them
During the self-assembly and setup of a delta printer, users may make a number of mistakes that will negatively affect the operation of the device:
- Incorrect printer calibration. It will lead to the occurrence of clearances and deviations in the geometry of the structure. And these troubles will cause serious distortions in the part during printing.
- Slipping of the rods from the magnets. This can lead to deformation of the printed product. Slipping of the rods from the magnets can be avoided by providing fixators under the rubber bands. They will prevent the hinge from slipping off the magnet.
- It is impossible to print an item to the full working height of the printer. This problem arises due to the incorrect placement of the printing head. It should be provided with separate space in the printer that does not occupy the useful working space.
By examining the features of the assembly and setup of the delta 3D printer, the user can independently create an apparatus for quick printing of complex structures. However, it should be noted that the assembly of such equipment is very complex and requires special knowledge.