Consumption of electricity by a 3D printer during operation
Any 3D printer uses electricity during its operation. The power consumption of the printer will depend on many factors. Let's consider the electricity consumption of various types of 3D printers, how to calculate the power, what this value depends on, and whether it is possible to reduce electricity consumption in any way.
- Power consumption of a 3D printer
- How many watts per hour?
- Is it possible to reduce power consumption?
Power consumption of a 3D printer
The nominal power consumption of a 3D printer shows the actual energy consumption of the device during operation. This indicator is directly related to the characteristics of the printer, especially its performance.
Depending on the method of creating workpieces, there are five types of 3D printers with specific printing technologies: SLA, SLS, FDM, DLP, MJM.
In terms of power consumption, printers with stereolithography laser-based (SLA) or digital light processing (DLP) technologies are considered the most costly, as these printers first need to heat the photopolymer and then expose the printed workpiece to ultraviolet laser. Many printers are also equipped with a heated bed, which additionally consumes electricity to heat the working surface. In the most productive models working with SLA and DLP technologies, the power consumption usually does not exceed 3 kW.
Models working with selective laser sintering (SLS), multi-jet modeling (MJM), and fused deposition modeling (FDM) are less energy-consuming. Such 3D printers during printing of workpieces require electricity only for heating the extruder. Some models may also be equipped with a heated bed.
3D printers printing products using SLS, MJM, or FDM technologies consume no more than 1 kW of electricity.
How many watts per hour?
How to calculate power?
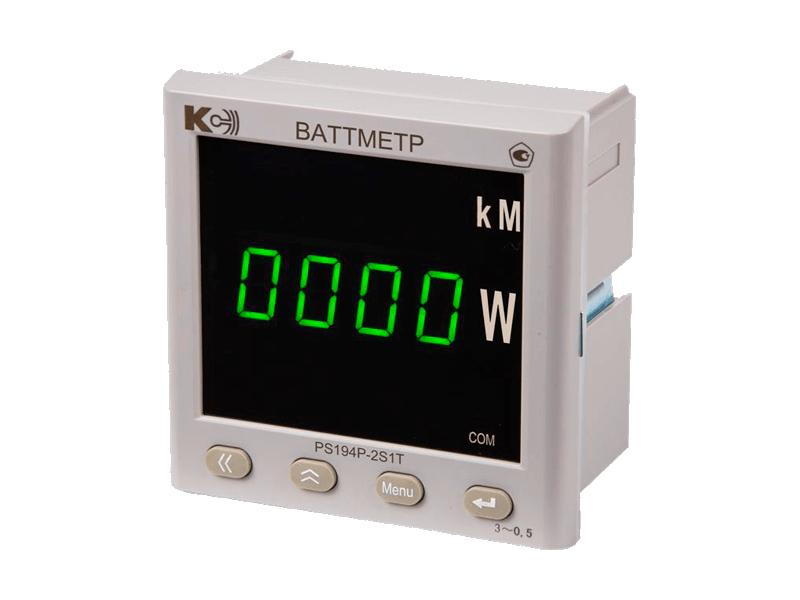
To calculate power consumption, it is necessary to use an electricity meter, wattmeter, or ammeter. When using the latter device, the data obtained will need to be converted into watts.
It is necessary to measure the power consumption by the extruder, the bed (if it has heating), electronic sensors and controllers, motors at idle and during operation. The measurements should be carried out over an hour.
Important! When measuring the printer as a whole, and not its individual parts, there may be an error in the calculations. Since the extruder and heated bed do not work constantly during printing, but about 50–60% of the total printing time. Therefore, 40–50% of the power consumption values by the bed and the extruder must be subtracted from the obtained electricity consumption values.
The obtained data is then added up. The resulting figure will show the nominal power of the printer.
What affects power?
The power consumption of a 3D printer directly depends on its technical characteristics. The presence of a heated bed and several extruders will increase power consumption.
The presence or absence of insulation on the bed will also affect power consumption. The installed insulation will allow you to maintain the necessary constant temperature of the surface while reducing the room temperature and not consuming electricity for additional bed heating.
Example of calculating power consumption
When measuring the electricity consumption of the Prusa I3 3D printer, a wattmeter was used.
As a result of the experiment, the following electricity consumption indicators were obtained:
- extruder — 37 W (37 W – 40% = 22.2 W);
- heated bed — 150 W (150 W – 50% = 75 W);
- motors operating — 10 W;
- motors at idle — 2 W;
- electronic sensors and controllers — 5 W.
Adding all the obtained indicators, we get the approximate power consumption of the 3D printer — 114.2 W.
Is it possible to reduce power consumption?
It is possible to reduce the power consumption of a 3D printer by not using a heated bed and several extruders. More economical power consumption will also be achieved by setting a lower extruder temperature during printing and reducing the temperature of the bed surface.
In addition, it is recommended to turn on the printer just before starting the print, rather than leaving it simply turned on. In idle mode, motors continue to work, albeit consuming little electricity.
In conclusion, it should be noted that 3D printing is not an energy-consuming technology. Even the most powerful 3D printers do not consume a lot of electricity. Therefore, when calculating the cost of a printed 3D item, electricity costs are usually neglected, and only the cost of the filament is taken into account.
Saving HTML Tags:, ,
- ,
- , ,
, , ,
,
,