Choice of extruder for 3D printer
The working head of a 3D printer is called an extruder. The plastic filament passes through it, melts, and is extruded through a nozzle onto the build plate. This is how objects are built layer by layer.
- Types of extruders for 3D printers
- Which extruder is the best for filament manufacturing?
- Review of extruders for 3D printers
- About the dual extruder on Ender 3 pro
Types of extruders for 3D printers
There are two types of extruders: direct and Bowden. They differ slightly in construction and have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Direct extruder
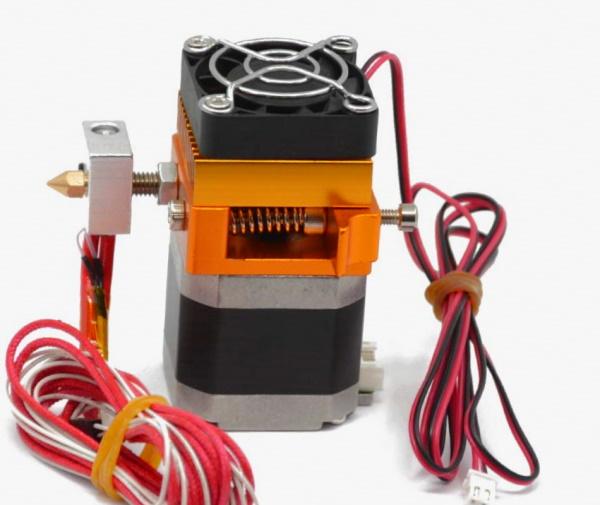
Direct extruders are positioned directly above the hot end. Thanks to this, the distance from the gear is minimal, ensuring more reliable operation with flexible filaments.
IMPORTANT. If the printer is equipped with a direct head, this does not mean it will print flexible filaments well. To ensure high-quality printing, it is necessary to monitor the position of the clamp and pay attention to the gear mechanism.
Direct extruders have more precise retraction control compared to Bowden. The location above the hot end significantly reduces the distance between the filament and the clamp, leaving less room for bending.
The print head on a direct extruder is bulkier, increasing inertia. A reliable rail construction is required for good print quality, and the large head size affects print speed.
Main advantages of direct extruders:
- Material replacement is easy and fast
- Minimal feed distance reduces errors
- Flexible plastics can be used at relatively high speeds
Disadvantages:
- Increased weight compared to Bowden
- More complex head design
Bowden extruder
When using a Bowden extruder, the gear and motor are assembled on the device's frame. The printing head is lighter compared to a direct extruder.
The main disadvantage of Bowden is that during filament movement through the Teflon tube connecting the hot end and the feed mechanism, it can deviate, especially when using flexible plastics. Printing settings and retraction size need to be adjusted experimentally.
The problem of friction also needs to be addressed. The filament must be pushed through the tube, requiring sufficient torque to complete this process.
REFERENCE. Most home delta 3D printers are equipped with Bowden extruders.
Advantages:
- Reduced weight of the carriage
- Smaller print head size
Disadvantages:
- Printing with flexible plastic is difficult
- Requires a powerful motor for material feed
- Printer error increases in proportion to the length of the tube
Which extruder is better to buy for filament manufacturing?
Currently, the cost of 1 kg of the cheapest filament is approximately $20, while plastic from reputable manufacturers can cost up to 50% more per 1 kg. Therefore, the question of manufacturing filament independently is very relevant.
Extruders for filament manufacturing:
- Limana Extruder. Invented by Hugh Liman, this device can produce 1.75 and 3 mm diameter filament with an accuracy of 0.01 mm, saving about 80% on filament purchases.
- Fisher or STRUdittle Extruder. This compact device can make ABS filament at a speed of 30–60 cm per minute. The accuracy does not exceed 0.05 mm with freely output filament. If using a reel that automatically winds the filament, the accuracy is reduced to 0.03 mm.
- Filabot Original. Known for its high performance, it can handle ABS, HIPS, and PLA. It can work with granular plastic or plastic waste, with a maximum particle size of 5 mm.
- FilaMaker. This device combines a crusher and extruder, producing up to 1 m of filament per minute with an accuracy of 0.05 mm. The only drawback is the high price of $1200.
- Filastruder. A relatively inexpensive extruder that can produce 1 kg of filament in 12 hours. The work speed ranges from 15 to 60 cm per minute, depending on the operating temperature, nozzle diameter, and material used. It is designed for ABS but can also be used for PLA, HIPS, and nylon.
Review of extruders for 3D printers
Below are the most popular extruders for 3D printers with detailed descriptions of their characteristics.
MK8
This is the most popular direct extruder. It is easy to install and use, suitable for most 3D printers, and costs about $15.
Technical specifications of the device:
- Used filament diameter: 1.75 mm
- Nozzle diameter can range from 0.2 to 0.5 mm
- Heater at 12 V and 40 W
- Operating speed: 4 cm per second
- Device weight: 450 g
- Operating temperature: from 190 to 250 degrees
E3D TITAN AERO
The main features of the E3D TITAN AERO:
- Direct drive
- Full-metal thermal barrier
- Maximum temperature: 285 degrees
- Transmission ratio: 3 to 1
- Suitable for flexible plastics
The device is easy to install and operate. The original costs about $170, but a Chinese analog can be purchased for around $40.
It includes:
- Standard or mirrored enclosure
- Heatsink
- Mounting connectors
- Fan
- Heater block
- Nozzle
- Teflon tube
- Thermal paste
- Idler lever
- Cable and thermistor cartridge
About the dual extruder on Ender 3 pro
A dual extruder allows printing with two filaments at the same time, eliminating the need to stop work to replace material.
Such devices are used to print models and supports with different materials. Supports are usually made of cheaper plastic and are removed after printing.
Water-soluble plastic is increasingly used for supports, saving time. Dual extruders are also used to print with different colors.
The Ender 3 pro printer supports the use of a dual extruder.
The extruder is one of the most important parts of a 3D printer. The type of device should be chosen based on the tasks that the printer will face.
Additional info: - Direct extruders typically have better control over retraction and can handle flexible filaments more reliably. However, they are generally heavier and bulkier, which can affect printing speed and require a more robust structure. - Bowden extruders are lighter and can potentially allow for faster printing speeds, but they may face challenges when handling flexible filaments and require more careful adjustment of print settings. They can also experience issues with filament friction and deviation.