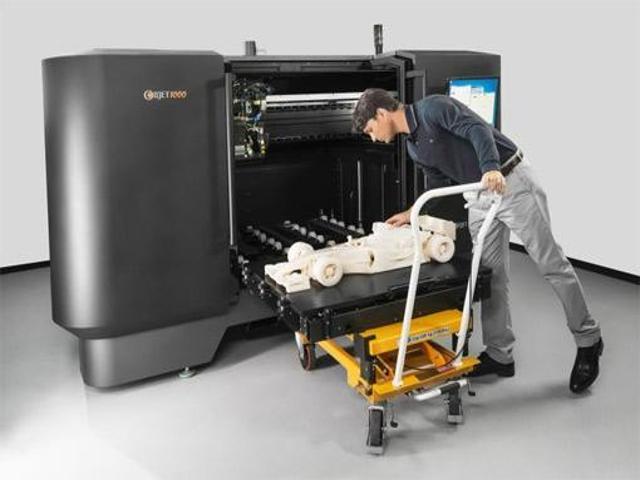
Best industrial 3D printers
3D printers are not only personal or professional, but also industrial, used in various industries. They have higher productivity, larger sizes, and of course, higher cost. But such equipment quickly pays for itself when used to its maximum capabilities.
- Industrial 3D printer
- Areas of application of industrial 3D printers
- Materials and main methods in industrial use of 3D printers
- Perspectives of using 3D printers in production
- Overview of the best industrial printers
Industrial 3D printer
In industry, 3D printing technology is often referred to as additive manufacturing. This manufacturing process is a complete opposite of the classic one, in which excess material is cut from the blank. In additive manufacturing, parts are created by layer-by-layer deposition.
Industrial 3D printer works with three-dimensional graphic files that contain the parameters of the future product. Models are created by scanning existing objects or manually using special programs.
The printer processes the received information and creates a structure from layers of sheet, powdered, or liquid material. The product is formed by sequentially joining the layers.
Areas of application of industrial 3D printers
In 3D printing technology, there are no waste materials, which is why it is beneficial to large factories and commercial enterprises. Three-dimensional printing has already firmly established itself in such industries as:
- military;
- aerospace;
- automobile;
- construction;
- medical.
This is because the technology allows the manufacturing of products with any geometry, which is impossible on normal industrial equipment.
Materials and main methods in industrial use of 3D printers
There are already more than 10 additive manufacturing methods in the industrial sphere. They differ in the materials they work with and the method of layer formation.
The most commonly used 5 methods in production are:
- Layer-by-layer deposition. Various thermoplastics, including polylactides, are used in the extrusion method.
- Electron beam melting. Powder and wire methods are used to create products from metal alloys.
- Laser metal fusion. Used in the creation of titanium alloys.
- Selective laser melting. It can be used to make parts from aluminum, stainless steel, and cobalt and chrome alloys. The finished products are comparable to those made by machining. But their production cost is lower.
- Selective laser sintering. With this method, parts can be made from polyamides, glass fiber reinforced, polystyrene, and reinforced carbon fiber.
Using 3D printing significantly speeds up the production cycle and reduces costs.
Perspectives of using 3D printers in production
Industrial giants have long been using 3D printing technology. For example, General Electric began manufacturing nozzles for rocket engines in 2015. Large printers are used to make parts from composite fiber and ceramics. Test results showed that such nozzles are several times stronger than their predecessors. This is due to the integrity of the structure. Previously, nozzles were assembled from 30 separate parts.
Rolls-Royce uses 3D printing in the production of aircraft engines. Individual engine components are made using 3D technologies. With printers, the shape of products can be easily changed without the need to modify the entire production line.
In 2016, NASA launched the Sinterhab project. They plan to "print" space complexes on the surface of the moon in the future. The agency also sees potential in printing spare parts directly on spacecraft. This will save hundreds of millions of dollars in cargo launches for transport rockets.
But the main thing is that 3D printing technology is already available to enterprises. Previously, only large companies could afford industrial printers, but now ordinary factories can use this equipment. On average, the price of an industrial printer varies between $5,000–$15,000.
Review of the best industrial printers
There are already more than 100 models available for purchase. The best of them are listed below.
Onsint SM200 3D printer
Onsint SM200 3D printer is a desktop industrial printer of Russian production that works by layer-by-layer laser sintering.
Features:
- Temperature stabilizer;
- CO2 laser (30 W);
- Scanner system;
- Optimal performance;
- User-friendly software.
- Power supply 220 V / 50 Hz
- File formats STL, OBJ, 3DS, CLI
- Sizes, mm 764x413x774 mm
- Software OnSint Studio
- Printing SLS
- Power consumption 3 kW
- Precise optics F-theta + scanner
- Working chamber area 200x200x200 mm
- Speed 20 mm/h
- Materials used polyamide, polystyrene, polypropylene
- Layer thickness from 80 μm
- Scanning speed up to 5 m/s
- Weight, kg 120
- Maximum workpiece size 180x180x180 mm
- Laser type CO2 (30 W)
Farsoon FS271M 3D printer
Farsoon FS271M 3D printer is a three-dimensional printer from the Chinese company Farsoon.
Features:
- Precision of products;
- High production capacity;
- Fiber laser 500 W;
- Gas filtration system;
- User-friendly AllStar software;
- Possibility of monitoring the process.
The printer has dimensions of 1750×1430×1860 mm and weighs 2033 kg. The working chamber is 275×275×340 mm. Selective laser melting (SLM) technology is used in the work. The built-in high-power fiber laser (500 W) perfectly melts metal powders of various types. Argon or nitrogen gas fills the chamber during operation.
- Certificates GB/T 15605-2008
- Power supply 380VAC, 50/60Hz, 8KVA
- Sizes, mm 1750×1430×1860
- Software MakeStar
- Laser spot diameter 70 μm
- Protective gas Argon / Nitrogen
- Material FS 316L, FS 17-4PH, FS 15-5PH, FS 420, FS 18Ni300, FS AlSi10Mg, FS TA15, FS CoCrMoW, FS CoCrMo, FS Ti6Al4V, FS IN625, FS IN718, FS GH3536, FS CuSn10
- Powder feeding module High-performance heat-resistant silicone rubber blade
- Laser power 500 W
- Scanning parameters Fully digital dynamic focusing, high-precision galvo-scanning system
- Printing SLM
- Supported file formats STL
- Build speed 20 cm3/h
- Laser type Yb-fiber laser
- Working chamber area 275×275×340 mm
- Layer thickness from 20 μm
- Weight, kg 2033
- Scanning speed 15 m/s
Go to product
3D printing is already actively used in industry. The technology was available several decades ago, but its cost at that time did not allow for the full use of additive developments. Now everything points to the fact that 3D printing in industry will not stop at what has been achieved and will become a new method for solving many engineering tasks.