ABS plastic: pros and cons of the material, features of printing
ABS plastic rightfully occupies one of the leading positions in the rating of the most popular materials for 3D printing. It is good both in terms of its physical properties and in terms of cost, which is why it attracts both enthusiasts and professionals.
ABS plastic is compatible with 3D devices that print using FDM technology. At the same time, the plastic should look like a thin thread wound on a spool, which is placed in a special compartment. When it enters the extruder — the printing head — the thread melts under the influence of high temperatures and is formed into layers of the future model.
More details on how this happens, the value of ABS plastic, and the conditions for working with it will be discussed further.
- About ABS plastic
- Pros and cons of printing with ABS plastic
- How to print with ABS plastic?
- Features of printing with ABS plastic
- Post-processing of ABS plastic after 3D printing
- Examples of printed products
About ABS plastic
The abbreviation ABS stands for acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene. It is the second most common material for 3D printing, second only to the more modern and user-friendly PLA.
Essentially, ABS is an impact-resistant technical thermoplastic resin based on three substances: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. In production, this copolymer is valued for its physical properties:
- non-toxic;
- easily dyed in any color;
- durable in conditions without direct UV rays;
- resistant to alkalis, household chemicals, aggressive cleaning agents;
- resistant to moisture, oils, and acids;
- does not melt at temperatures up to 103 °C (some modifications up to 113 °C);
- densely packed.
The applications of the material are practically unlimited. ABS plastic is used in mechanical engineering, the production of large and small household and electrical appliances, industrial objects, furniture, sports equipment, toys, stationery, musical instruments, and much more.
In recent years, the demand for ABS plastic has significantly increased due to the growing popularity of 3D technologies. The material is ideal for amateur-level work using standard desktop devices.
Pros and cons
ABS is an easily accessible, inexpensive, high-quality material that is compatible with many types of 3D devices from different manufacturers. Plastic products are durable, long-lasting, and resistant to negative environmental conditions. But like any material, it has its drawbacks.
So, the advantages of ABS plastic include the following characteristics:
- affordability (one spool of filament weighing 1 kg will cost about $20–50);
- durability (the service life of ABS parts is longer than PLA parts);
- minimal deformation under heavy loads with subsequent return to the original form;
- easy processing using various methods (manual grinding, mechanical polishing, chemical smoothing, and others);
- high mechanical strength;
- moisture resistance and inertness to acids and oils;
- flexibility and elasticity;
- a wide choice of color solutions;
- high thermal capacity.
The contrast of such a range of advantages is the number of material drawbacks:
- sharp, persistent smell of melting plastic during printing, so it is not recommended to use the 3D printer in a residential building;
- difficulty in use (melting requires a temperature of about 230 °C, and for some printers, this is the maximum working temperature);
- deformation as it cools (compression);
- delamination with non-uniform cooling of the product;
- inaccessibility of the same high print resolution as with PLA.
If desired and necessary, most of these drawbacks can be avoided by purchasing high-quality plastic from a reliable manufacturer. But the price of it will then be higher.
How to print with ABS plastic?
To print models from ABS plastic, you will need a printer with FDM technology, a spool of filament in the desired color that is compatible with the device, a well-ventilated room where people are not constantly present, and a model of the future model on a digital medium.
The spool with the thread is inserted into a special compartment, and its end is directed to the extruder. The printer is then prepared in accordance with the instructions, the necessary settings are set, and the printing of the model begins.
REFERENCE! Due to the sharp smell of melting plastic, it is not recommended to stay in the room where the printer is installed. You can monitor the printing process online by turning on the webcam beforehand.
The settings of the printer are particularly important for print quality.
Temperature and parameters for printing ABS
ABS is printed at a relatively high temperature, around 240 °C. For some models, this is the maximum heating temperature.
IMPORTANT! A full-metal hotend is not required to preheat the extruder to 240 °C.
The optimal printing temperature is determined by trial and error. In addition, the temperature of the print surface is also important: it is usually recommended to stick to the norm of around 80 °C.
Approximate optimal parameters for printing with ABS are:
- melting temperature — 240–260 °C;
- layer thickness — 20% less than the diameter of the nozzle;
- print surface temperature — 80–115 °C;
- plastic feed rate — 0.85–0.95;
- printing speed — 30–60 mm/s.
One of the main problems in working with ABS plastic is the detachment of the model from the print platform due to low adhesion. This usually does not happen if the platform has heating: this helps to avoid deformation of the product during cooling and, accordingly, detachment from the platform.
If the platform does not have heating, other solutions are found: a solution of ABS plastic in acetone, hairspray, glue stick, or special glue for 3D printing.
Features of printing with ABS plastic
In principle, working with ABS plastic is not difficult if you know its strengths and weaknesses and prepare well for the process. The features of printing and post-processing of products made of this material affect the quality, strength, and durability of the resulting models.
Filament drying
ABS plastic is hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture, like any material for FDM printers. The presence of water in the filament thickness means that the structure of the plastic is disrupted, the device can be damaged during printing, and the quality of the finished product will be low.
Signs of filament moisture are as follows:
- characteristic crackling and extrusion noises;
- low strength of finished models;
- weak adhesion of detail layers;
- uneven extrusion lines;
- printing defects: oozing, bubbles, dents;
- blurred surface of the product.
If the filament shows all signs of moisture, it does not need to be thrown away. It can be saved by drying, and it is desirable to do this as soon as the fact of water getting into the spool is established.
No special drying devices are required for filament drying. You can use a regular oven: for this, the spool with the thread is placed in the oven for 4–6 hours at a temperature of 80 degrees. The longer the thread stays in the oven, the drier it will become.
IMPORTANT! The spool with the filament needs to be placed in the oven only after it has been preheated to the required temperature.
An alternative method is drying in a fruit or vegetable dryer. The temperature and drying time are the same.
Heating the print platform
Heating the print platform is a mandatory condition for good adhesion. If the platform is not hot enough or is completely cold, the end result will be unsatisfactory: the product simply will not adhere to the platform, or will detach from it with subsequent layers. As a result, time and material are wasted in vain.
Overall, when working with ABS plastic, it is recommended to follow the rule: the higher the platform temperature, the better. But if the first layer still peels off, it is necessary to either reduce the printing speed or increase the extruder temperature.
For the first layer, the optimal platform temperature is around 115 degrees, and for the second and subsequent layers, up to 100–105.
Is a fan needed when printing ABS?
One of the most controversial issues in the field of 3D printing. Here it is important to remember 2 points:
- a fan is needed if the printing time for each layer is less than 20–30 seconds;
- it is better to use vertical, spherical, rather than frontal cooling (for uniformity).
The use of a fan when working with ABS plastic is not mandatory, since by setting the optimal printing parameters and temperature for the extruder and print platform, it is possible to prevent the product from spreading, warping, and cooling.
However, if it is necessary to significantly speed up printing, the fan will help maintain the quality of the product.
Post-processing of ABS plastic after 3D printing
For beginners who are just starting to work with ABS plastic, the results of their work may seem unsatisfactory. Finished plastic products, after being removed from the platform, have a rough, uneven surface, with visible layer lines, and sometimes gaps.
To bring the part to the proper appearance, it is necessary to carry out its post-processing.
Printing ABS on a cold platform
Printing ABS on a cold platform will lead to a poor result: the product simply will not adhere to it. To ensure a tight adhesion of the first layer to the print surface, special sticky compounds should be used, or the surface should be treated with a solution of ABS and acetone.
But keep in mind that the smell when printing will be even stronger, so it is undesirable to be in the room during the process.
Removing support structures
Support structures are necessary for those products with angles of 45–70° and more. In this case, the support elements support these angles and overhanging elements and prevent them from sagging, tipping, or deforming.
Supports can be soluble or insoluble depending on the material they are printed from.
Soluble supports can be removed in two ways:
- with water (PVA);
- with special compounds (limonene, isopropyl alcohol, or their mixture).
Insoluble supports are removed manually using mechanical means such as knives, pliers, and various brushes. It is important to be careful and handle the finished product gently, as there is a risk of damaging the model.
Chemical polishing
Chemical polishing using acetone is one of the simplest and most effective methods to smooth the surface of a product. The process is as follows:
- lay paper towels in a deep container;
- pour a little acetone on top so that the towels completely absorb it;
- place a layer of foil on top;
- place the finished product on the foil and close the container tightly with a lid.
After a few hours, the container must be opened and the foil with the model should be gently removed and left for some time in an open area to allow the acetone to evaporate.
IMPORTANT! Do not touch the piece immediately after opening the container, as the top layer of the model will be partially dissolved and very brittle.
Mechanical grinding and polishing
Mechanical polishing of ABS products is necessary to hide the gaps between layers. For polishing, you will need sandpaper of various grits or a special composition — polishing paste.
The product should be treated with paste or sandpaper slowly, carefully, and wearing a protective medical mask.
Gluing
Very often, the actual size of the finished product significantly exceeds the volume of the 3D printer. In this case, it is possible to print the necessary parts separately and then glue them together. The order of actions for this is as follows:
- Clean the surface from dust and dirt.
- Moisten both parts with acetone.
- Press the parts together tightly and hold them in this position until the acetone completely evaporates.
ATTENTION! Increasing the area of the parts being glued together increases the strength of the connection, so it is desirable to provide places for junctions in the 3D model consisting of several parts.
Puttying
Puttying of ABS elements is required in cases where voids are formed. To fill them, a mixture of filament and acetone at a ratio of 1:2 is used. If the voids are too deep, the amount of plastic can be increased.
Also, for filling the voids of ABS 3D products, epoxy resin-based putty can be used.
Painting
The best adhesion to ABS is provided by acrylic paints. Fortunately, they are widely available, come in a wide variety of colors, are easy to work with, and provide high-quality coloring, even for small details.
REFERENCE! If a different type of paint is chosen, it will be necessary to mix it with acrylic primer.
The paint should be applied using an airbrush or aerosol. Beforehand, it is necessary to test the paint on a small piece of the same filament-made product.
Inserting metal parts
To give durability to the finished products, brass inserts with threads are usually inserted into them. If they are provided by the construction, it will be necessary to make sockets of the appropriate diameter or perimeter for them during printing.
The insert should be inserted halfway into the socket, and then gently pressed down with a well-heated soldering iron. After the insert takes the required position, the parts must be allowed to cool completely before using as intended.
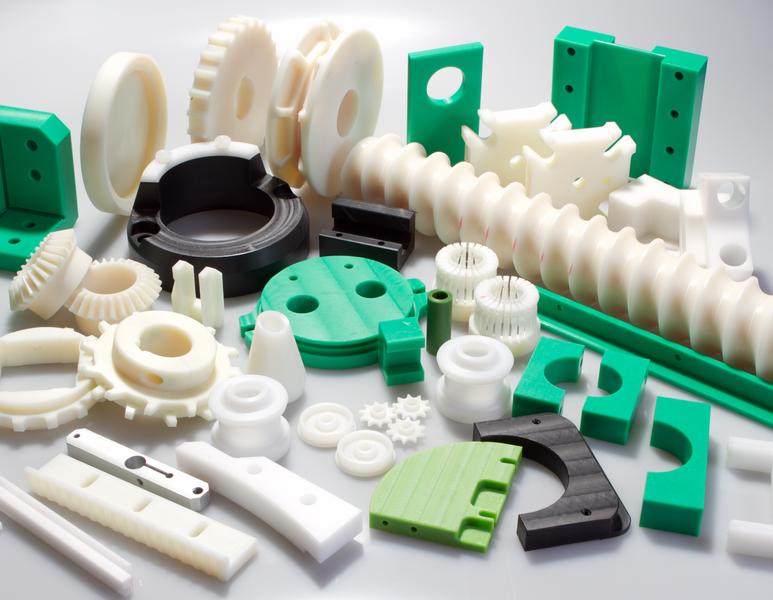
Examples of printed products
In conclusion, ABS plastic is an affordable and therefore popular material for FDM printers, with its advantages and disadvantages. It produces strong and durable elements that do not deform over time and withstand negative environmental effects, ranging from moisture to mechanical impacts.
Maximum quality of finished products can be achieved by selecting the optimal printing parameters and correctly performing post-processing.