3D prototyping and its types
Before launching a new product into production, most companies first conduct its testing. New technologies help significantly reduce costs and time spent on this task. Often, 3D prototyping is used for this.
- 3D Printing Prototyping
- Types of prototypes
- Rapid prototyping technologies
- Stages of 3D model prototyping
- Requirements for prototyping
- Software
3D Printing Prototyping
The creation of a working model is a complex process, during which a product sample is created. It is suitable for evaluating functionality and properties, as well as for demonstrating to the target audience. This is done before the product is launched into mass production.
What is it?
Prototyping is the creation of a complete or partial model of a product that is being prepared for production.
Principle of operation
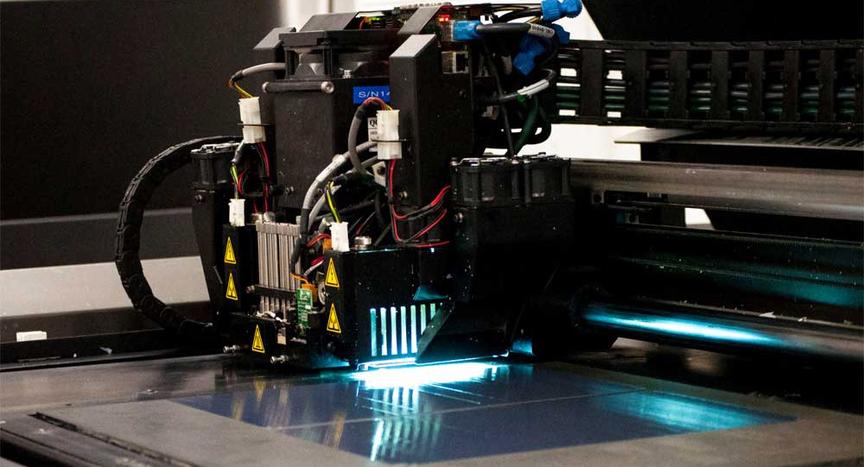
Thanks to 3D prototyping technology, the time spent on creating prototypes has been significantly reduced. This allowed additive manufacturing to obtain the status of a "bypass technology." The principle of the technology is to create a physical object based on a digital 3D model. First, a CAD model is created, and then it is printed on a 3D printer. Prototyping often occurs using inexpensive printers, although different materials can be used.
Application
Prototyping is used in various industries, such as custom production, creating building structure models, toy and souvenir manufacturing, exhibition product samples, spare parts production, and more. In medicine and dentistry, printers are used to print prostheses, organ models, surgical instruments, templates, and more.
Types of prototypes
Prototypes are divided into the following types:
- Industrial. This type includes models of components of various mechanisms and devices. The highest accuracy and quality requirements are imposed on these 3D prototypes.
- Consumer. Often produced in the form of a product or its packaging.
- Presentation. Used in design, construction, and architecture. For example, this could be a building model.
- Transport. A scale model of a car or other vehicle is created.
Rapid Prototyping Technologies
These are the various prototyping technologies:
- Stereolithography (SLA). This technology uses a liquid photopolymer with the addition of reagents, which is polymerized by an ultraviolet laser. Layers are created sequentially on a moving substrate.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). The technology involves the layered production of a model using powder. The material is uniformly distributed on the plane, after which individual areas are heated by a laser. The powder material can be plastic, metal, glass, investment wax, or ceramic.
- Multi-Jet Modeling (MJM). Devices for this technology are developed by 3D Systems. The model is created using standard inkjet printing principles. The material is fed through nozzles located on the print head, with consumables being preheated and then fed into the extruder, which prints the layers of the part.
- Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM). The method involves layering film, which is then cut with a laser or special blade.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). In this technology, each layer is applied with melted material, which is extruded through a nozzle. Often, plastic is used for printing, but other materials such as metal can also be used. Objects created by this method have low quality, but it is the cheapest to implement.
Stages of 3D Model Prototyping
The prototyping process includes the following steps:
- First, a computer model of the future object is created.
- After that, a prototype is made using 3D printing.
- The finished prototype is tested.
- If necessary, the product is adjusted and corrected.
Modeling
3D modeling occurs on a computer using special programs for engineering 3D graphics. Drawings, sketches, graphics, and necessary technical documentation are used to create the model.
Master Model Creation
After modeling, a master model is printed. A product prototype is created that should cover all basic needs.
Model Testing
The master model is tested for compliance with specified requirements, such as appearance, ergonomics, correct forms, etc., depending on the object's intended usage.
Adjustment
If any inaccuracies or discrepancies to requirements are found during testing, they are corrected in the computer model. After this, all previous stages are repeated.
Prototype Creation
If the master model passes all tests, a prototype is created. This is a fully functional product.
Requirements for Prototyping
A quality prototype should be:
- Visual
- Accurate
- Functional
Accuracy mostly depends on the quality and professional 3D modeling.
Software
Best software for prototyping:
- Wings 3D. This program belongs to advanced tools for 3D modeling, allowing the creation of highly accurate models. Wings 3D has a customizable interface and can save files in most 3D formats.
- Open SCAD. This is free 3D modeling software. Open SCAD is a 3D compiler that displays details in three planes.
- AutoDesk 123D. The program has a wide range of tools for CAD and 3D modeling. It allows the creation of projects and visualization of almost any 3D models.
- 3DReshaper. This is an affordable and fairly simple modeling tool used in various industries, such as art, construction, shipbuilding, mining, etc. 3DReshaper has built-in support for different textures and scenarios, making 3D modeling much easier.
- form·Z pro. This program is great for furniture and house designers, as well as designers. It allows the creation of objects of any complexity and is known for its structured modeling capability for the processing of unique forms, making object construction based on mesh, which remains parametric during compression and stretching, much easier.
The use of 3D printing in prototyping has significantly reduced costs and time spent on work. The right type of technology can make the production process faster, more efficient, and reliable for any industry.